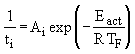
where Eact represents an overall activation energy and TF is the temperature of the combustion environment. Ignition time depends upon the chemical structure of the hydrocarbons, as it has to facilitate gaseous reactions.
The onset of combustion causes slight thermal decomposition. The heat released produces further fuel evaporation from the fuel droplet. Then the viscosity of the residue increases as large paraffins are broken down, side chains are stripped from asphaltenes and similar molecules, undergoing condensation to form carbon-like structures.
The final amount of oil mass remaining in the solid residue represents between 0.5 and 10 % of the original drop mass.


